Monocrystalline solar panels now surpass polycrystalline solar panels in efficiency - by a significant margin.
Most of the top 20 models of domestic solar panels in 2020 are monocrystalline.
The cause of this is a new technology that makes monocrystalline solar panels more efficient.
They also cost about the same as many Tier 1 polycrystalline panes, so it may appear there is little reason to select the poly design.
However, in our perspective, the cost premium imposed by Panasonic, LG, and Sunpower for their monocrystalline panels isn't justified by their additional functionality.
Homeowners should also look at top-quality monocrystalline brands like Trina Solar, Canadian Solar, JA Solar, Jinko Solar, and Longi.
A while back, prices of polycrystalline solar panels were 20-30% lower than monocrystalline solar panels.
But now many solar panel manufacturers have moved their furnace tech to monocrystalline cells instead of polycrystalline cells, making the cost similar.
That said, there is no underlying defect in polycrystalline solar panels that should steer you away from them, so long as they are providing at a reasonable price from a reputable Tier 1 manufacturer.
New solar cell technologies are under development now to compete with polycrystalline and monocrystalline solar panels.
In this post, we discuss the differentiation between monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels - in terms of aesthetics, price and energy efficiency.
This article's objective is to help you select a right kind of panel for your application.
What are Polycrystalline and Monocrystalline solar panels?

The polycrystalline and monocrystalline panels are both made from crystalline silicon.
Polycrystalline and monocrystalline solar panels are both made from a arrangement of silicon cells. These types of silicon solar panels are known in the industry as 'mono' and 'poly' panels.
In 2020, almost every consumer will use one of these 2 kinds of crystalline solar panels. Most are monocrystalline with layers of amorphous silicon to increase efficiency and to enhance performance at high temperatures.
Key Facts About Each Kind Of Solar Cell
Monocrystaline Panels

This is the most developed and oldest of the three solar cell technologies used today.
Monocrystalline panels, as the name implies, are created from a single continuous crystal structure.
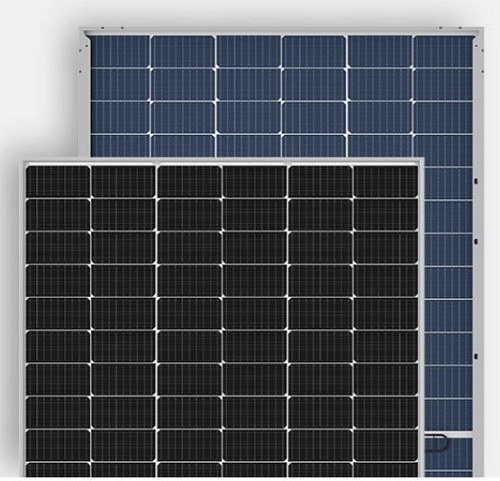
A monocrystalline panel is identified by all solar cells sharing a single, flat color.
Monocrystalline Panels are created by the Czochralski method, where a silicon crystal' seed' is set in a vat of molten silicon. The seed is then drawn up with the molten silicon, forming a stable crystal structure around the seed called an ingot'.
The ingot of solid crystal silicon created is then finely sliced into what is known as a silicon wafer. This is then made into a cell.
The Czochralski process leads to big cylindrical ingots.
Four edges are cut out of the ingots to fabricate silicon wafers.
A substantial quantity of the original silicon ends up as waste.
Polycrystalline Panels

The Polycrystalline, also referred to as multi-crystalline, is a newer technology, and its manufacturing method varies.
Polycrystalline panels start as a silicon crystal' seed' put in a vat of molten silicon.
Rather than drawing on the silicon crystal seed upward as is done for monocrystalline cells, the vat of silicon is allowed to cool.
It's the cooling that creates distinctive edges and grains within the solar cell.
Between 2012 and 2016, polycrystalline cells were believed to be inferior to monocrystalline cells since they were less efficient.
That said, because of the cheaper method by which they were created, coupled with only slightly lower efficiency, they enjoyed a significant market share in residential installations.
With continued quality enhancements, polycrystalline cells have helped move the conventional 60-cell polycrystalline solar panels from 240W to 300W over the last five years.
What are Thin-film Solar Panels? Why not use them on residential installations?

Thin-film solar panels are a completely new technology, very different than mono and polycrystalline panels.
They're made from a different sort of silicon, called amorphous silicon (a-Si) and occasionally other substances with semiconductor properties called CIGS (copper indium gallium selenide solar cells).
Thin-film solar panels are much cheaper to create than panels comprising cells using crystalline silicon due to lower efficiency.
Manufacturers of thin-film panels include Sanyo, Kaneka, and Solar Frontier.
First Solar, a large American producer, is a manufacturer of thin-film CIGS panels.
Some of these firms still sell these panels for industrial applications, but their efficiency and power output per square foot makes them unsuitable for consumer rooftops.
The price advantage they enjoyed over panels has disappeared since the purchase price of earning crystalline silicon cells has dropped.
A thin film panel can be recognized as having a black appearance without the standard cell outlines you see on a panel's surface.
Thin-film panels are produced by depositing a photovoltaic substance on a solid surface, such as glass.
The photovoltaic material that is used varies, and multiple blends of materials have been successfully used commercially.
Examples of popular photovoltaic substances used include:
Each of the above is known as panel 'types,' but all come under the category of a thin-film panel.
Thin-film cells have a name for being the most powerful solar panel technology, but they have the lowest efficiency.
As lately as a couple of years back, thin-film efficiencies were in the single digits.
Scientists have recently attained 23.4% efficacy with thin-film cell prototypes, but commercially available thin-film panels usually run in the 10-13% range.
Benefits of Monocrystalline Solar Panels

Best Efficiency
Monocrystalline panels have the highest efficiency rates because they are produced from the highest-grade silicon.
Their single-cell structure produces minimum resistance to the flow of electricity once the electrons are excited from sunlight.
The Sunpower X22 Collection of monocrystalline panels, with a maximum efficiency of 22.6%, is the most potent residential solar panel available in 2020.
Solar panels' efficacy will likely continue to improve.
In 2019, both Longi and Trina Solar declared new world records for their specific types of monocrystalline cells. Though not yet in a production version, Trina cell claims a mobile efficiency of over 24.5 percent.
Ideal for Smaller Roofs
Monocrystalline silicon solar panels are space-efficient. Their higher efficiency means that they produce more electricity each foot.
This means they can create the same amount of energy with fewer cells, so smaller multi-story homes can rely on them.
Long Lifespan
Monocrystalline panels have a very long lifespan.
Many solar panel manufacturers offer a 25-year warranty on their monocrystalline solar panels.
These panels often last more than their warranty life because they are made from crystalline silicon, an extremely stable material.
High-Efficiency Levels Regardless of Heat.
Monocrystalline panels are far more efficient in warmer weather.
As temperature goes up, electricity production falls. This lack of output is not as severe in monocrystalline panels compared to polycrystalline solar panels.
However, in practice, the gap is small. The level to which production from each kind of solar panel falls as temperature rises is called the temperature coefficient and is mentioned with each panel's specifications.
Disadvantages of Monocrystalline Solar Panels
High Price
Monocrystalline panels are the most costly.
As more companies of polycrystalline solar cells have turned their metal furnaces to build monocrystalline cells, the cost premium for monocrystalline panels over polycrystalline panels has dropped.
Benefits of Polycrystalline Solar Panels

Less Expensive
The procedure used to make silicon is easier and costs less.
Highest Heat Tolerance
Polycrystalline panels tend to have a greater temperature coefficient than solar modules built with monocrystalline cells. This implies that as heat increases, the output for this sort of cell will fall less. Though, in practice, these differences are minor.
Disadvantages of Polycrystalline Solar Panels
Lower Efficiency
The efficiency of polycrystalline-based solar panels is generally 14-16%.
Due to lower silicon purity, polycrystalline solar panels aren't quite as effective as monocrystalline panels.
This means that you'll have to cover a larger area to put out the same amount of electrical power as you would using a solar panel created of monocrystalline silicon.
This doesn't imply monocrystalline solar panels work better than those made with polycrystalline silicon - they simply require less space to achieve that.
Not As Easy On The Eyes
Thin-film and monocrystalline solar panels are far more aesthetically pleasing as they have a more consistent look in comparison to the spotted blue color of polycrystalline silicon.
Benefits Of Thin-Film Solar Panels

Disadvantages Of Thin-Film Solar Panels
How Much Do Polycrystalline And Monocrystalline Modules Cost In 2020?
A residential solar energy system that uses polycrystalline or monocrystalline solar panels prices will cost about $3 per watt or about $18,000 for a standard 6 kW system.
After the solar tax credit is applied, the cost of solar installation using either polycrystalline or monocrystalline solar panels can be reduced to to $14,000.
In 2020, There Remains A Substantial Cost Difference Between Panel Types.

For the Chinese Tier 1 solar panel, the cost difference between polycrystalline and monocrystalline panels is 1-2 cents per watt.
At the wholesale level, poly and mono modules from this category - examples being Canadian Solar Longi, Trina, or Jinko - are around 50 cents per watt.
Big Price Range Within Mono Panels
The most notable thing about monocrystalline panel pricing is the high cost premium commanded by the best mono manufacturers, SunPower and Panasonic.
At the wholesale levels, these solar panels cost in the 75 cent to $1 per watt range.
This is a significant 50-100% premium over Chinese Tier 1 panels that are of similar build quality but only slightly less efficient.
The Installed Price Of Chinese Tier 1 Mono Vs. Premium Mono Panels And Poly Panels
By the time solar firms add a margin, this implies premium mono panels used in professionally-installed systems will cost between $3.00-$3.50 per watt.
The all-installed price for Chinese Tier 1 modules is far lower, in the $2.30 to $2.80 per watt range.
Given the average home requires a 7kW solar system, high quality branded mono panels wind up costing $3,000-$5,000 more - that's a massive price premium for panels that are not likely to generate more power and last just as long.
While the three biggest brands are all well-made, excellent and efficient panels, their price premiums will be difficult to maintain when the federal tax credit ends, when people need to pay 100% of their home solar system themselves.
Will New Solar Cell Technologies Impact The Kind Of Panels?
It's likely that within a couple of years, there will be new cell types available that use different cell technologies within one cell to generate significantly enhance efficiencies.
In April 2020, researchers in the NREL labs in Colorado announced they had developed a solar cell that attained a conversion efficiency of 47% using concentrated sunlight and 39% using unconcentrated sunlight. This used a six-junction cell that contained layers of different kinds of semiconductor material.
This implies that the difference between mono and poly models may become blurred in the coming years, as cells may comprise multiple layers of different materials.
How Significant Is The Choice Of Cell Type (Mono Or Poly) When Purchasing Solar Panels?
Choosing between monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels is not the most important aspect when purchasing solar panels.
As a matter of functionality, in 2020 all of the quotes you get for solar panels will likely be based on monocrystalline solar panels.
We regard two things as more important than the solar panel type when choosing solar panels for your home:
1. Selecting a right brand
A good brand of panel is a company that significantly invests in the quality of its production process, as well as its reputation.
2. Choosing the right installer
You need to pick an excellent local solar installation company to set up the solar system for you.
Header | Monocrystalline solar panels | Polycrystalline solar panels |
|---|---|---|
Cost | More expensive | Less expensive |
Longevity | 25+ years | 25+ years |
Efficiency | More efficient | Less efficient |
Aesthetics | Solar cells are a black hue | Solar cells have a blue-ish hue |
Major manufacturers | Canadian Solar Sunpower LG Hyundai SolarWorld | Hanwha Kyocera Hyundai SolarWorld Trina |